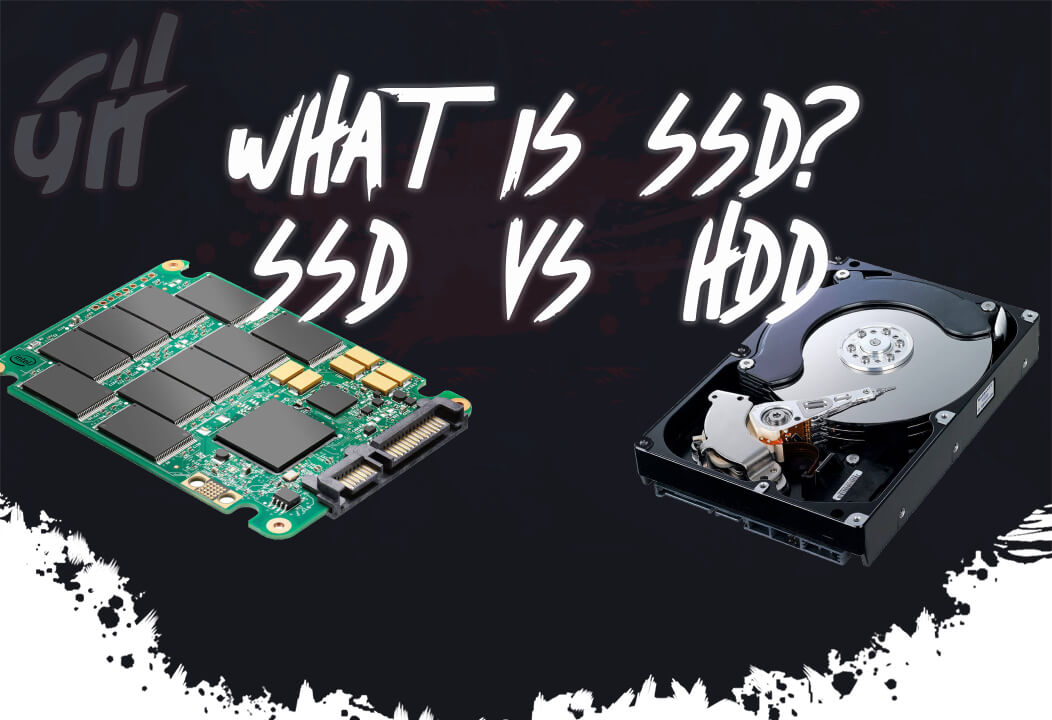
What is SSD? SSD vs HDD
Introduction Of SSD
SSD (Solid-State Drive) is a computer storage device introduced in 1991 by a company named ScanDisk. Solid State Drive uses integrated circuit assemblies to store data persistently on instantly-accessible memory chips, typically using flash memory, and works as a secondary storage in the hierarchy of computer storage as an alternate to traditionally used Hard Disk Drives in computers that use mechanical platters and a moving read/write head to access data.
Life Expectancy – SSD Lifespan
According to the most recent estimate after the joint study between Google and University of Toronto where both researchers tested SSDs in a multi-year span, It was concluded that the lifespan of SSD is 10 years and its age is primary determinant of when an SSD stopped working so the average age can be shorter depending on the use and quality. But yours might outlive other SSDs if you’re lucky ;)
SSD Size And Speed
When it comes to storage capacity, SSDs come in different storage sizes ranging from 80 GigaBytes to 30.7 TeraBytes as for now. And the average speed when talking about read and write, An SSD can read data around 550 MB/s and write data around 520 MB/s with SATA interface. Some newer SSDs even deliver around 600 MB/s speed and even more when connected with a faster interface such as PCIe.
SSD is an expensive storage device when it comes to store data in a large amount. So, If you want to use it for personal computer, the more decent and economical approach would be to use SSD only for the operating system and necessary softwares, use other storage media for your personal data and games.
Types Of SSDs
Depending on how the SSD is connected to the computer there are four types of SSDs which are commonly used: 2.5″, mSATA, M.2 and PCI-E that use the older slower serial data connection, mSATA port, the newer faster M.2 connection and PCI Express connection, respectively. Moreover, Different SSDs also use different types of flash memory.
The original flash memory type is SLC and it stores one bit of data per memory cell. SLC is still used in some enterprise SSDs where maximum reliability is valued over cost. MLC and TLC are newer types that store more data in the same amount of space sacrificing a bit of reliability for cheaper cost and more storage capacity.
3-D or V-Nand is a further enhancement to fit more data in less space involving stacking a bunch of memory cells on top of each other.
SSD vs HDD
When you want to store data on your computer you have two reasonable options. You can go with an old slow but cheap option called a Hard Disk Drive or you can go with this newer faster but more expensive option called a solid-state drive or SSD. For a long time the only way to store information on your PC in a long term easily accessible manner was to use a hard disk drive. Which is the technology that dates all the way back to the 1950s.  These refrigerator-sized IBM 305 shown in picture was used to held 3.75 megabytes of data each, just about the amount of data used to store one photo taken by a modern smartphones.
These refrigerator-sized IBM 305 shown in picture was used to held 3.75 megabytes of data each, just about the amount of data used to store one photo taken by a modern smartphones.
Hard drives also came a long way when it comes to their size. From these half occupying room size storage cabinets to small size hard disk drives which are in use till now.
How They Work

Inside a commonly used hard drive there’s a moving arm that writes data onto a spinning disk. Out of all the types of memory in a modern computer hard drives are still the most cost-effective way to store large amounts of data, but they’re also the slowest by comparison.

The SSDs use flash memory which involves no moving parts. flash memory is much faster than disk-based memory but it comes with a higher cost. Thankfully flash memory technology evolves quickly and prices continue to drop while storage sizes are on the rise making SSDs an increasingly viable alternative to hard drives
How Much SSD Is Faster Than HDD
When it comes to speed they’re about 10 times faster than hard drives. while still being more than 10 times slower than Ram. Moreover, They have the benefit of working as a long-term storage option just like a hard drive. even if they can’t currently store as much data and they can’t do it as cost-effectively.
Noise Difference
SSDs are silent because they have no moving parts. With SSD, PC makes less noise and don’t take up much power due to which the computer doesn’t get heated. So you can do heavy tasks with less temperatures, this gives SSD another big advantage over hard drives. If your PC is showing high temperatures or usage, installing SSD will definitely lower the burden slightly in this case. Furthermore you’d be able to work peacefully after getting rid of HDD, Which can often be heard reading or writing with their spinning disk and moving parts.
Power Usage
SSDs use less power. This is more helpful for laptop users as it doesn’t affect negatively on the battery life. Although it doesn’t normally matter as much on a desktop but it can slightly reduce electricity consumption.
In the times of such rapidly growing technology, We highly recommend getting an SSD if you’re still using old hard disk drives. Or you should at least consider using it as boot drive by adding a small SSD to install your operating system. You will see a undeniable increase in performance and it’s the most noticeable PC upgrade for the user.
The Real-World Benefits Of Having An SSD
An SSD will load everything on your PC faster than a hard drive. For example, if you install your operating system on an SSD, your PC will boot up significantly faster. PC world benchmark booting windows on the same computer took 63 seconds with a classic 7200 RPM hard drive and only 23 seconds with an SSD, almost three times faster.
Going from a system with just a hard drive, to one that includes an SSD is probably the single most noticeable upgrade you can perform. I like to compare it to switching from dial-up internet to broadband. It’s that big a difference to benefit from the speed of SSDs.
While not having to sacrifice storage space. Many people include both an SSD and a hard drive in their PC. They’ll install their operating system and their most commonly used applications on the SSD and use the hard drive to store files such as videos, images, games and other documents.
How reliable are SSDs?
Should you be worried about storing your important data in these little magic boxes? The short answer is that SSDs are at least as reliable as hard drives on a desktop. That is a way better choice for a laptop because they don’t have any moving parts to break. If they get dropped, endurance was a problem with early SSDs.
Because the individual memory cells have flash memory, we’re out faster than the magnetic disk of a hard drive with modern SSDs; this is no longer an issue for normal users, even with low endurance.
Modern SSD could withstand writing a hundred gigabytes of data every single day for twenty years. That’s a lot. I’m a fairly heavy computer user and I write about five gigabytes of data per day. So, I don’t have to start worrying about the endurance of my SSD for at least three hundred and eighty years.
The reliability of an SSD is very similar to the rest of the parts in your computer SSDs contain solid-state capacitors, firmware, a PCB electrical can vector, and all of the other little parts that can and do occasionally fail. Whether your data is on an SSD or hard drive, always backup anything important.